gated heart pool scan
What is a Gated Heart Pool Scan?
A Gated Heart Pool Scan (GHPS), also known as Radionuclide Ventriculography (RNV) or Multi-Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scan, is a specialised nuclear imaging test used to assess the heart's blood pumping ability. It provides detailed images of the heart’s chambers and their movement by tracking a radioactive tracer injected into the bloodstream.
This test is non-invasive, painless, and provides highly accurate measurements of heart function, particularly the ejection fraction (EF)—the percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each heartbeat.
Who is Suitable for a Gated Heart Pool Scan?
A GHPS is recommended for individuals who:
- Have Heart Failure or Cardiomyopathy – to assess how well the heart functions.
- Have Undergone Chemotherapy – to monitor potential heart damage caused by certain cancer treatments (e.g., anthracyclines).
- Have Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) – to evaluate how well the heart muscle is pumping after a heart attack.
- Require a Pre-Surgical Heart Function Assessment – for individuals undergoing major surgery, particularly valve replacement or organ transplantation.
- Have Unexplained Symptoms – such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations, which may indicate underlying heart disease.
- Are Being Evaluated for a Pacemaker or Defibrillator – to determine if they need a cardiac device for heart rhythm issues.
Benefits of a Gated Heart Pool Scan
A GHPS provides several advantages over other heart imaging techniques:
- Highly Accurate Ejection Fraction Measurement – More precise than echocardiography, especially in patients with complex heart conditions.
- Early Detection of Heart Dysfunction – Helps detect cardiac impairment before symptoms appear, especially in chemotherapy patients.
- Non-Invasive & Painless – No surgical procedures are involved, and the scan is painless.
- Minimal Radiation Exposure – The amount of radioactive tracer used is small and safe.
- Objective & Reproducible Results – Unlike echocardiograms, which depend on operator skill, GHPS results are consistent and can be compared over time.
- Useful for Long-Term Monitoring – Helps track the progression of heart conditions and the effectiveness of treatment.
Conditions Diagnosed by a gated heart pool scan
A GHPS can help diagnose and monitor several heart-related conditions, including:
- Heart Failure (HF) – Determines the severity of heart failure by measuring the heart’s pumping efficiency.
- Cardiomyopathy – Identifies abnormalities in the heart muscle function.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) – Assesses heart function in patients with blocked or narrowed arteries.
- Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity – Detects early signs of heart damage caused by certain cancer treatments.
- Heart Valve Disease – Evaluates the impact of faulty heart valves on heart function.
- Congenital Heart Disease – Identifies structural defects present from birth.
- Arrhythmias & Conduction Disorders – Assesses how well the heart’s electrical system coordinates contractions.
Further Information Provided by a Gated Heart Pool Scan
A Gated Heart Pool Scan provides detailed functional insights about the heart, including:
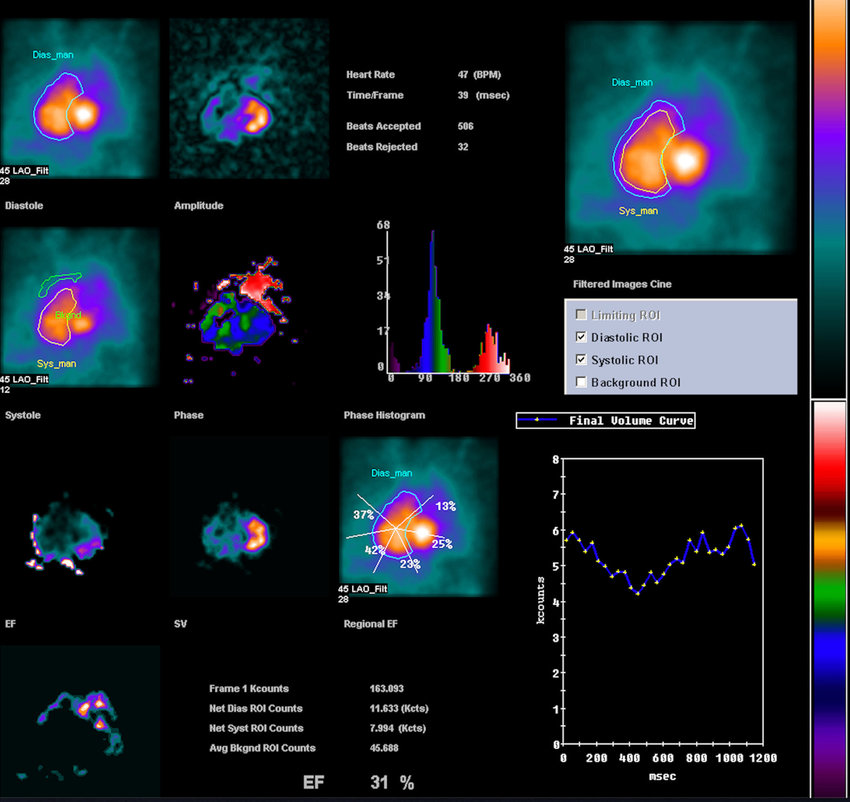
- Ejection Fraction (EF) – The percentage of blood pumped from the heart with each contraction, crucial for assessing heart function.
- Wall Motion Abnormalities – Identifies if parts of the heart muscle are not contracting properly due to previous heart attacks or conditions like cardiomyopathy.
- Cardiac Output – Measures how much blood the heart pumps per minute, helping evaluate heart failure.
- Ventricular Volumes – Determines the size of the heart chambers, which is useful in detecting enlarged hearts (dilated cardiomyopathy).
- Synchronisation of Heartbeats – Assesses if the heart’s contractions are properly coordinated, which is essential for patients considering pacemakers or defibrillators.
Preparation for a Gated Heart Pool Scan
What to Bring:
- Referral Letter – Provided by your doctor.
- Medicare Card & Health Insurance Details – If applicable.
- List of Medications – Include all prescribed and over-the-counter medications, as some may affect the scan results.
What to Wear:
- Comfortable, Loose-Fitting Clothing
- Minimal Jewelry
Dietary & Medication Restrictions:
- Fasting is usually unnecessary, but some facilities may ask you to avoid caffeine or certain medications before the test.
- Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, as alternative imaging methods may be considered.
How Long Does It Take?
- The entire process typically takes 1 to 2 hours, but it may vary depending on the facility and the patient’s condition.
Gated Heart Pool Scan Procedure
The GHPS is a non-invasive imaging test conducted in the following steps:
- Injection of Radioactive Tracer: A small amount of Technetium-99m is injected into a vein. Sometimes, a blood sample is taken and mixed with the tracer before re-injection. The tracer binds to red blood cells, allowing clear imaging of heart movement.
- ECG Electrodes Placement: Small, sticky ECG electrodes are attached to the chest. These electrodes monitor the heart’s rhythm to synchronise imaging with heartbeats.
- Scanning Process: The patient lies still on a scanning table under a gamma camera. The camera detects radiation from the tracer and creates detailed images of the heart’s function. The scan captures images at different angles for 15-45 minutes.
- Completion & Review: Once imaging is complete, the electrodes are removed. A specialist will analyse the images and prepare a report for your doctor.
What about the injection?
You need two injections to attach the radio-tracer to the red cells in your blood. The first injection attaches to red cells, and the second injection (of radio-tracer) attaches to the first. There are no side effects; you will not feel tired or dizzy, and you can drive a car.
What about the pictures?
Immediately after the second injection, a series of pictures is obtained. The camera takes four photos of your heart at different angles. An ECG must be performed during the pictures to synchronise with your heart's beating. Depending on how well your heart is beating, the pictures take about 40 to 60 minutes.
What to Expect After a Gated Heart Pool Scan?
Immediate Post-Scan Instructions:
- No recovery time is needed, and patients can drive home afterwards.
- Drink plenty of water to help flush out the radioactive tracer from the body.
- The amount of radiation used is low and considered safe, but avoid close contact with pregnant women and infants for a few hours.
When to Expect Results?
- Results will be available the following day after 2pm.
- The doctor will discuss the findings and recommend any necessary treatment or follow-ups.
Potential Side Effects:
- Most patients experience no side effects.
- Rarely, some may have mild discomfort at the injection site.
- See medical attention if you experience unusual symptoms like rash, dizziness, or swelling.
Gated Heart Pool Scan Prognosis
A normal ejection fraction (EF) of 55% or higher indicates that the heart is pumping efficiently. A Reduced EF (below 40%) may indicate heart failure or cardiomyopathy.
Treatment may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or, if abnormalities are found, procedures like pacemakers or heart surgery. Follow-up GHPS scans may be required to monitor heart function over time, especially for chemotherapy patients or those with heart failure.
Gated Heart Pool Scan Risks
A GHPS is a low-risk, noninvasive procedure. It is safe for most patients and has no major side effects.
What if a Gated Heart Pool Scan is Delayed?
Delaying a Gated Heart Pool Scan can have serious implications, particularly for those with suspected or existing heart conditions.
- For Heart Failure Patients:
- Delays may prevent early detection of worsening heart function, leading to untreated progression.
- Late diagnosis may increase hospital admissions and limit treatment options.
- For Chemotherapy Patients:
- Many cancer treatments can cause heart damage (cardiotoxicity) over time.
- Without timely monitoring, heart function may decline unnoticed, increasing the risk of heart failure.
- For Post-Heart Attack Patients:
- If heart function is not assessed in time, necessary medications or procedures (like stents or surgery) may be delayed.
- For Patients Requiring Surgery:
- Major surgeries often require a pre-operative heart assessment.
- A delay in the scan could postpone surgery or lead to undetected risks during the procedure.
Gated Heart Pool Scan Costs
Bulk billed. No out-of-pocket costs.




