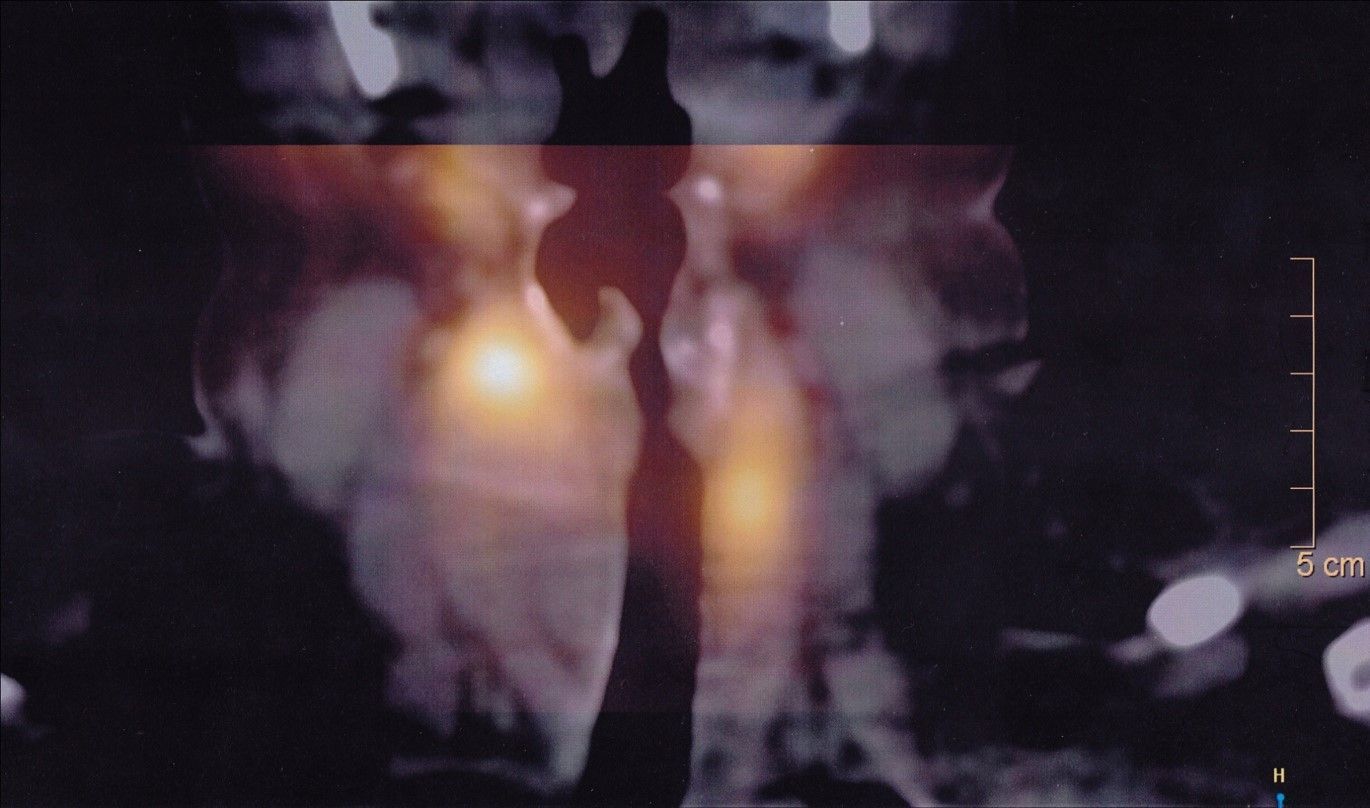
thyroid scan
What is a Thyroid Scan?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck. It produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall body functions. The thyroid scan shows the shape and size of the thyroid, how well it is functioning overall, and whether lumps in the thyroid are working normally or not.
The scan is typically performed using:
- Technetium-99m: The thyroid absorbs these substances, allowing the scan to capture images of the gland’s activity.
- Ultrasound: This method provides detailed images of the thyroid’s size, shape, and nodules but does not assess function.
Who is Suitable for a Thyroid Scan?
A thyroid scan may be recommended for individuals experiencing:
- Unexplained thyroid symptoms, such as weight changes, fatigue, or rapid heartbeat.
- Swelling or lumps (nodules) in the thyroid gland.
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), causing symptoms like nervousness, excessive sweating, and rapid heart rate.
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), leading to fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity.
- Thyroid cancer suspicion, based on physical examination or abnormal blood test results.
- Monitoring of previous thyroid conditions, including thyroid cancer follow-up or assessment of treatment effectiveness.
This scan is generally not suitable for:
- Pregnant women (due to radiation exposure).
- Individuals allergic to iodine or radiotracers.
Benefits of a Thyroid Scan
A thyroid scan offers several benefits, including:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Helps distinguish between thyroid disorders, such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and nodules.
- Non-Invasive: A relatively simple and painless procedure that provides essential diagnostic information.
- Detection of Thyroid Nodules: Identifies nodules and determines whether they are functioning ("hot" or "cold" nodules).
- Cancer Screening: Assesses whether a thyroid nodule is potentially malignant.
- Guides Treatment Decisions: Helps doctors determine if surgery, medication, or radioactive iodine therapy is necessary.
- Monitors Thyroid Function: Evaluates how well the thyroid is responding to treatment.
Conditions Diagnosed by a thyroid scan
A thyroid scan can help diagnose various thyroid-related conditions, including:
- Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
- Thyroid Nodules and Tumors
- Thyroid Inflammation (Thyroiditis)
- Goiter (Enlarged Thyroid Gland)
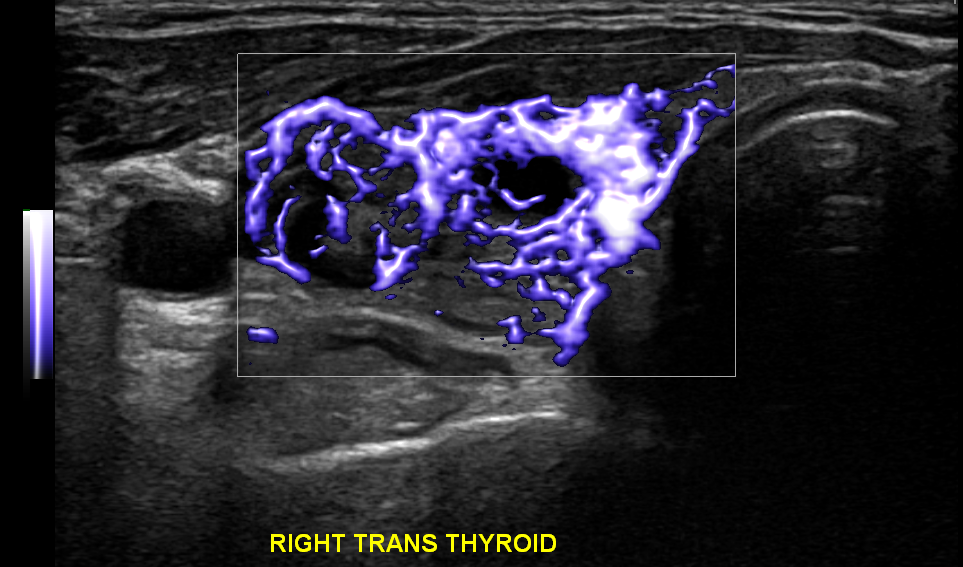
What Further Information Can a Thyroid Scan Show?
A thyroid scan provides detailed insights into the structure and function of the thyroid gland. It can reveal:
- Size and Shape of the Thyroid – Helps detect an enlarged or shrunken thyroid gland, which may indicate underlying conditions such as goitre, thyroiditis, or cancer.
- Thyroid Nodules – Differentiates between “hot” (overactive, usually benign) and “cold” (underactive, potentially malignant) nodules.
- Thyroid Functionality – Determines whether the thyroid is producing hormones at a normal, high, or low rate.
- Cancerous Growths – Assists in evaluating whether a lump or mass in the thyroid is suspicious for cancer.
- Metastatic Thyroid Cancer – Can check for the spread of thyroid cancer beyond the gland (in cases of known thyroid malignancy).
- Effectiveness of Treatment – Used in post-treatment follow-up for conditions like Graves’ disease or thyroid cancer, ensuring therapy success.
Preparation for a Thyroid Scan
Proper preparation is important for accurate results. Patients should follow these guidelines:
What to Bring
- A referral from your doctor.
- Any previous thyroid-related imaging or test results.
- A list of current medications, including supplements and iodine-containing drugs.
What to Wear
- Comfortable clothing with an open neckline to allow easy access to the neck area.
- Avoid jewellery, especially necklaces, as they may interfere with imaging.
Dietary Restrictions
- Avoid iodine-rich foods and supplements a few days before the scan (e.g., seafood, dairy, and iodised salt).
- Depending on the type of test, fasting may be required before the scan. Your doctor will provide specific instructions.
Medication Adjustments
- Certain medications, such as thyroid medications, anti-thyroid drugs, or contrast agents containing iodine, may need to be stopped before the scan.
- Inform your doctor about any medications you take, including herbal supplements.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Please inform the doctor or the technologist if there is a chance you are pregnant or are breastfeeding.
How Long Does a Thyroid Scan Take?
- The procedure typically takes 30 to 60 minutes.
- If a thyroid uptake test is included, it may take several hours or require a follow-up visit for additional imaging.
Thyroid Scan Procedure
A thyroid scan is a non-invasive and painless test that involves the following steps:
Administration of Radioactive Tracer
- You are given a small injection into one of the veins in your arm. After the injection, there is a delay of about 15 minutes until the scan. There are no side effects; you will not feel tired or dizzy, and you can drive a car.
Imaging Process
- After the 15-minute break, pictures of the thyroid are taken. This takes about 15 minutes.
What to Expect After a Thyroid Scan?
Is it painful and are there any side effects?
No. The injection does not cause side effects or reactions. It does not contain iodine and is, therefore, safe for people allergic to radiological contrast injections. Although you must remain still during the scan, the procedure is painless.
Can I take my normal medication?
Yes. Take all of your normal medications.
Can I eat and drink on the day of my test?
Yes, you do not need to fast before this test. However, drinking plenty of fluid will help the bone tracer clear from your system more quickly.
Immediate Post-Scan Instructions
- You can resume normal activities immediately unless your doctor advises otherwise.
- If you were given a radioactive tracer, you may be instructed to:
- Drink plenty of fluids to help flush the tracer from your body.
Possible Side Effects
- Mild nausea or dizziness (rare).
- Allergic reactions to the tracer are extremely rare.
- If an injection was used, slight discomfort may occur at the injection site.
When to Expect Results
- Results will be available the following day after 2pm.
- Your doctor will discuss the findings and recommend further tests or treatments if needed.
Thyroid Scan Risks
A thyroid scan is considered safe, but like any medical procedure, there are minimal risks:
- Radiation Exposure: The amount of radiation used is low and generally not harmful to most people. However, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers should avoid the test unless necessary.
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms may include itching, rash, or swelling at the injection site (if an IV tracer is used).
- Discomfort or Side Effects: Some patients report mild nausea, dizziness, or headache, but these effects are uncommon.
- Iodine Sensitivity: Patients with iodine allergies or those on a low-iodine diet should inform their doctor before the scan.
What if a Thyroid Scan is Delayed?
Delaying a thyroid scan may not be critical in some cases, but in others, it can lead to complications:
- Undiagnosed Hyperthyroidism or Hypothyroidism: Without proper diagnosis, thyroid hormone imbalances may continue, leading to fatigue, weight changes, heart palpitations, or even serious conditions like thyroid storm (in severe hyperthyroidism).
- Missed Detection of Thyroid Cancer: If a nodule or tumour is present, delaying the scan could allow it to grow, making treatment more complex.
- Uncontrolled Goiter Growth: An enlarged thyroid goitre) may continue growing, potentially causing difficulty in swallowing or breathing.
- Worsening Symptoms: Conditions such as Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, or thyroiditis can progress if left undiagnosed and untreated.
- Delayed Treatment Planning: If surgery, medication, or radioactive iodine therapy is needed, postponing the scan delays important medical decisions.
When to Prioritize a Thyroid Scan?
- If you experience rapid or unexplained changes in weight, energy levels, heart rate, or neck swelling, seek medical attention promptly.
- Early scanning can determine whether further tests (e.g., biopsy) are needed if a thyroid nodule is detected.
- If you have a history of thyroid cancer or a strong family history, timely scans are crucial for monitoring.
Thyroid Scan Costs
- Medicare Coverage: Bulk Billed. No out-of-pocket cost.




